3.4.1 Cell defaults
To change the default cell settings, select the menu "Cells → Cell defaults":
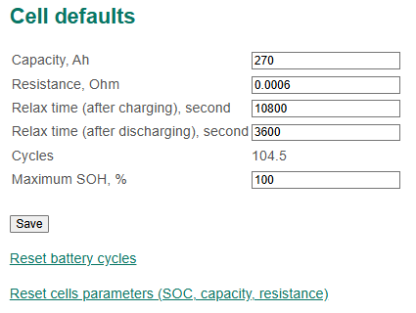
Cell default section
In this section:
- Capacity – nominal capacity of cells, Ah;
- Resistance – nominal (maximum) internal resistance of the cell, Ohm;
- Relax time (after charging) – a relaxation time after charging, second;
- Relax time (atfer discharging) – the relaxation time after discharging, second;
- Cycles – a number of charge-discharge cycles;
- Reset battery cycles – a command to reset charge-discharge cycles;
- Reset cell parameters (SOC, capacity, resistance) – a command to reset cells state of charge, capacity, and resistance.
The values “Capacity”, “Resistance”, “Cycles” are used to calculate the SOC of cells and battery.
The values of “Relax time” are used to determine the state of the battery. If the battery is in a state of relaxation, the system recalculates the voltage on the cells to the state of charge of the battery.
The “Reset cell parameters” command is used for starting-up and adjustment of battery.
3.4.2 SOC estimation
The BMS Main 2.x board calculates the state of charge of the battery (SOC) using two algorithms:
- by open circuit voltage;
- by current and voltage.
It is recommended to use the algorithm of calculation of SOC by voltage and current.
To change the parameters of the algorithm for calculating the battery SOC, select the menu "Cells → SOC estimation":
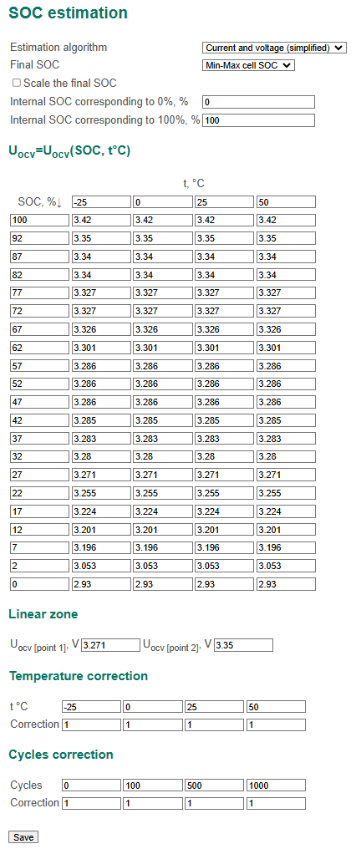
SOC estimation section
In this section:
- Estimation algorithm – SOC calculation algorithm:
- Voltage – by open circuit voltage;
- Current and voltage (simplified);
- Current and voltage (enhanced);
- Final SOC – a method of calculating the battery SOC:
- Minimum cell SOC – the battery SOC is assumed to be equal to the minimum SOC of cells;
- Average cell SOC – the battery SOC is assumed to be equal to the average SOC of cells;
- Scale the final SOC – flag to scale the battery SOC by the following values;
- Internal SOC corresponding to 0% – battery SOC that sets to be 0%;
- Internal SOC corresponding to 100% – battery SOC that sets to be 100%.
- Uocv = Uocv(SOC, t °C) – the dependence of the cell open circuit voltage Uocv on SOC and the cell temperature (selected for specific batteries, can be established experimentally – see section Determining the discharge characteristic);
- Linear zone – linear zone of dependence Uocv = Uocv(SOC, t °C):
- Uocv [point 1] – starting point of the linear zone;
- Uocv [point 2] – end point of the linear zone;
- Temperature correction – the dependence of battery capacity on temperature;
- Cycle correction – the dependence of battery capacity on the number of charge-discharge cycles.
The SOC calculation algorithm for voltage calculates SOC cells based on the tabular dependence Uocv = Uocv(SOC, t °C) .
The SOC calculation algorithm “Current and voltage (simplified)” works as follows:
- if I = 0, the battery is in a state of relaxation and the cell voltage Uocv is outside the [Uocv[point 1]; Uocv[point 2]], the SOC calculation based on the tabular dependence Uocv = Uocv(SOC, t °C);
- in any other cases, the SOC value is proportional to the charge (coulomb) passed through the battery (current time integral).
The SOC calculation algorithm “Current and voltage (enhanced)” differs from the simplified algorithm by online correction of effective capacitance. When using this algorithm, it is necessary to fine tune the tabular dependence Uocv = Uocv (SOC, t °C).
